Strategic, technological, regional foresight
Table
of contents
- What is foresight?
- Why is foresight research so important?
- What sort of information does foresight research deliver?
- Why perform foresight research?
- Methods applied in foresight research
- What techniques we use in foresight research?
- Who should use foresight research?
- Our clients
- Why choose our offer?
- Foresight research – price list
- FAQ
Foresight relies on active creating of pictures (visions) of the future. It differs from forecasting, as it does not provide ready-made future solutions, but offers scenarios – possible variants of future development. It is a research process, which differs from other types of research, due its four elements which are combined only in case of foresight.

- Orientation towards shaping of the future
Foresight goes beyond analysis or pondering potential development pathways, as it most of all support interested actors in active shaping of the future. Sheer analysis of possible variants, unrelated to specific actions are not considered to be foresight. For this very reason, foresight activities should only be caried out in such cases, when shaping of the selected aspects of the future is truly feasible.
- Openness to the alternative future scenarios
Foresight assumes that the future cannot be taken for granted. Hence, it can develop in different ways, which are shaped, among others, by actions of various subjects and consequences of decisions taken at present. Therefore, to some extent, there is some freedom of choosing from alternative, feasible scenarios – possible variants of development. This, in turn, increases the possibility of preferred future vision to really take place.
Participative approach
Foresight is not performed by a narrow group of experts and scientists, but it involves various groups of stakeholders, who identify relevant problems. Foresight results are widely disseminated to a broad audience, whose opinions are an important part of the whole research.
Multidisciplinarity
Foresight’s main principle states that problems we face cannot be properly understood, if they are reduced to only one dimension. The process must be compatible with the perspective of numerous fields of science. Hence, foresight is an approach that mirrors the reality, with all the relevant variables, both quantitative and qualitative.
Why is foresight research so important?

Future, as an outcome of currently taken actions and made decisions, is a key resource for development, widely used at present.
Even though the change by its very nature is a continuous, ongoing and unavoidable process, nowadays it has become particularly intense due to exponential growth of the technological progress.
Both the environment we live in and the market structure, value chains and production technologies evolve in shorter time intervals than ever before.
In relation to development, future is indeed a space, which can only be described using such a dedicated methodology as foresight. It inspires to consider future as something we can create or shape. Hence, it is neither future telling, nor forecasting, aiming for revealing the future, as if it is already set in stone.
The main advantage of foresight is unravelling different development scenarios (in plural) and indicating drivers, which determined selected aspects of the future. The power of foresight does not lie in visions, which completely change the current reality. This power lies in what the target audience can do about those visions; how it can prepare for the opportunities, which the future will bring; what approach it should adopt and which factors ought to be analysed.
What sort of information is provided by foresight research?
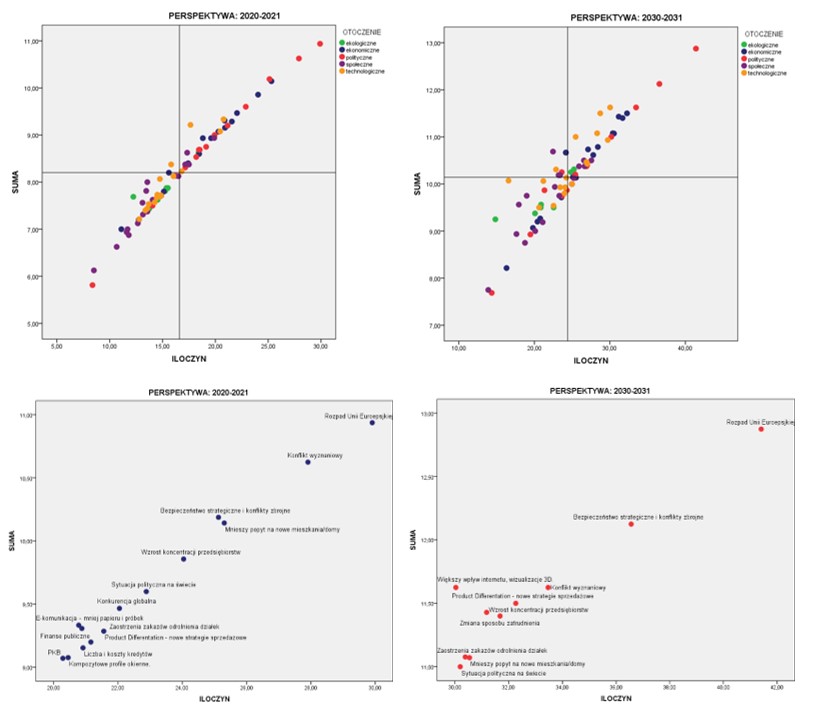
Foresight provides development scenarios for selected industries, companies, or organisations.
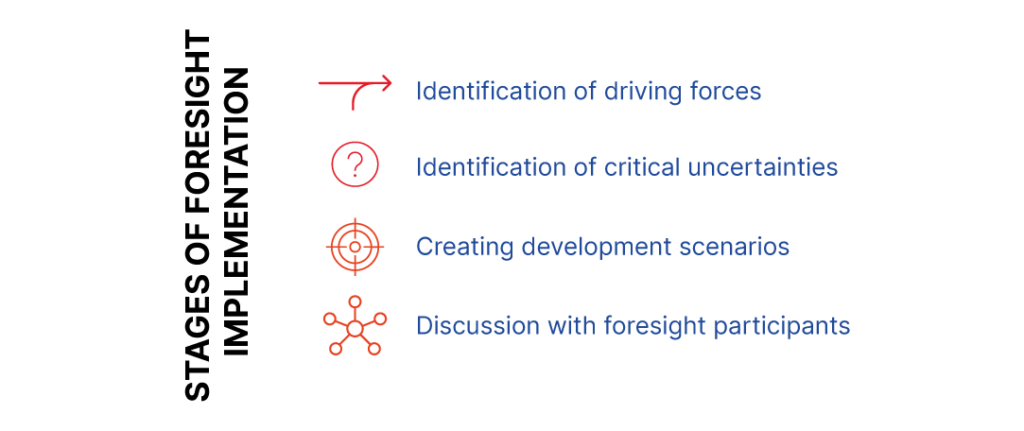
In order to create them, an interdisciplinary research team should be built. Then, four stages of foresight, during which the key information is obtained, should be completed.
Stage 1 – Identifying driving forces
Stage 2 – Indentifying uncertainties
Stage 3 – Elaborating the scenario matrix
Stage 4 – Discussing with stakeholders
Why carry out foresight?
Foresight is a kind of a “safety net”. It allows us to determine the environmental factors and the market needs and compare them with the strategy of a company or other organisation. Each new idea should be thoroughly thought through, and before launching it ought to be researched in terms of its validity and cost-effectiveness.

Methods used in foresight research
One of the characteristics of foresight research is a variety of applied research methods. They are often categorised in accordance with four dimensions of the foresight diamond: creativity, co-sharing, facts and expertise.
STEEP analysis
STEEP analysis is based on the assumption that the development depends on numerous factors aggregated in five different, yet interwoven areas. Hence, it is an assessment of the surroundings, aiming at identifying drivers which influence the analysed sector in five areas: social, technological, economic, ecological and political.
Expert panels
Expert panels are teams of specialists from selected industry, involving 12 – 20 people who discuss selected problem. Their work lasts from 3 to 18 months.
Delphi method
Delphi method is most frequently used in foresight research. It relies on a series of surveys, within the same group of experts, who do not communicate with each other.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming, as a form of group discussion, is normally used at the forecasting stage of foresight research.
Cross-impact analysis
Cross impact analysis, also known as mutual impact technique, relies on placing all the considered factors in one matrix. Because of this, it is possible to determine the likelihood of specified events in terms of the possibility of their occurrence or the time of happening, considering different orders. This analysis is related to the Delphi method because many elements of one method (the impact size and its importance) is established using another.
- Benchmarking
Benchmarking in foresight research can be used in order to define points of reference in analysis of selected aspects.
Trend extrapolation
Trend extrapolation is a trend predicting method, which takes into account macro environments. It assumes that the processes will evolve.
Survey research
Individual spontaneous surveys with the foresight workshop participants (without suggesting answers) are carried out at the beginning. They enable grasping the largest possible number of factors, to be analysed from different angles (social, technological, economic, ecological or political context).
Scenario matrix
A scenario matrix is a visual representation of all the scenarios that have been built, considering the drivers and insecurity factors, which emerged during the research process.
What techniques do we apply to foresight research?
We use the following techniques in our foresight research projects:
CATI
Telephone interview
CAWI
Online survey
PAPI
Pen and paper survey
Face to face FGI
Group interviews
Online FGI
Group interviews
Ethnography
Observation and description
IDI
Individual face to face in-depth interviews
ITI
Individual online in-depth interviews
CAPI
Computer-Assisted Personal Interviews
Dyads, tryads
Small group interviews
User tests
Product tests, consumer’s assessment
DR
Desk research, secondary data analysis
MOBI
Face-to-face survey on mobile devices
Eye tracking
Biometric research – tracking the eye movement
Face tracking
Biometric research – facial expression analysis
Mystery e-mailing
Mystery shopper – testing customer service via email
Mystery calling
Mystery shopper – testing customer service via phone
Mystery shopping
Mystery shopper – testing face-to-face customer service
Project design methods
Design thinking, iterative design
Motion tracking
Motion capture - XSENS, Vicon, Kinect
Auditorium questionnaire
A questionnaire filled in by a specific group being in the same room
EMG
Biometric research – analysis of micro expression of facial muscles
EEG
Biometric research – brain activity analysis
GSR
Biometric research – the galvanic skin response
Who should make use of foresight research?

Enterprises planning a long-term development
Innovators who want to implement new technologies
Institutions tackling social/demographic challenges
Public authorities and regional governing bodies planning development of the country, industries, regions, cities etc.
Organizations/companies who need to elaborate strategy for development, transformation, expansion
Each organisation/company, which would like to prepare for the future
So far, we have had the opportunity to work with organisations, whose goal was to build scenarios for an industry development. As a first organisation in Poland, we have had an opportunity to carry out foresight research for the woodworking industry.
Why choose our offer?

Since 1996, we have been carrying out research for companies and public institutions. Owing to the highest quality standards, professionalism and acquired experience, we take great pride in high indicator of returning customers.
We know how to best obtain the information necessary for effective planning of strategic actions.
We will be happy to answer your questions and suggest research methods most suitable for each individual case. We kindly invite you to get familiar with our offer.
Foresight research- Price list
The foresight research, which we carry out, is customised and tailored to each client’s needs. Therefore, we strongly recommend contacting us, in order to obtain a detailed price list.
FAQ
Foresight is a tool used for active building of the future. It inspires to consider future as something we can create or shape.
This research allows us to embrace the future by identifying drivers in the environment and preparing scenarios based on those drivers.
The timeframe for the research is discussed individually with each client. However, the average project duration is 6-24 months. This time might be reduced or prolonged, depending on the adopted methodology and the planned scope of analysis.
Short- or long-term forecasts are concentrated on estimating the scale of a single event, parameter or indicator. Their maximum timeframe is a few years. However, foresight refers to longer timeframe, ranging from 5 years to several decades and it factors in a wide range of activities.
In each case the cost of research is discussed individually with a client, in accordance with adopted methodology and the scope of the research project.
Companies, who are planning to build a long-term market strategy, social organisations or industry associations, working in a certain field, state and local authorities.
We take a personalised approach to each research project, for this reason methods and techniques are tailored to specific research problem.
We support all the industries

































